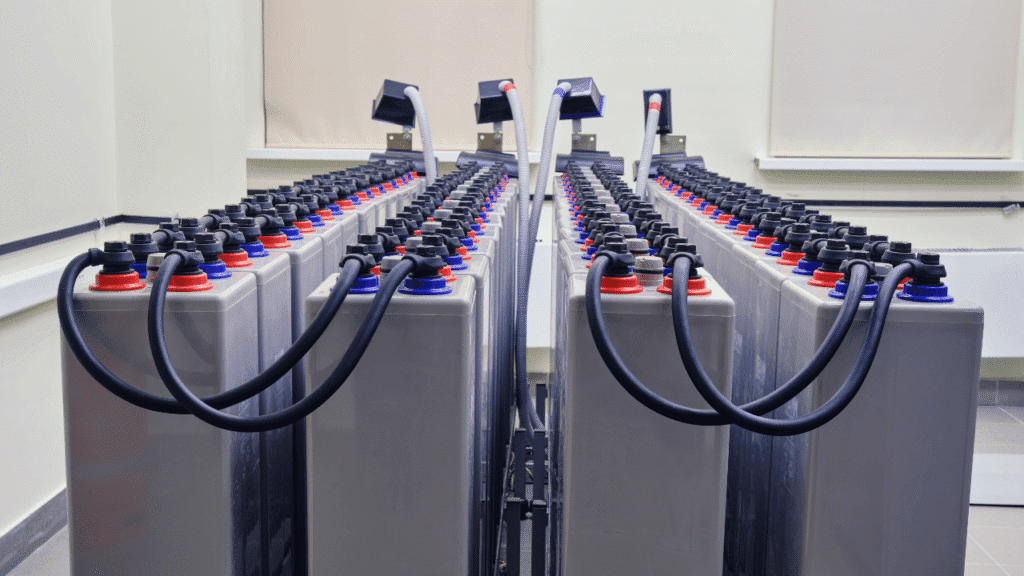
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is an important component of electronic systems today which delivers a secondary power source during outages, fluctuations, or failures. The main function of a UPS is to provide reliable, consistent power to equipment and reduces downtime in production and operations.
In today’s digitally-converged world, uninterruptible power supply systems are found in industries and applications such as information technology (IT), healthcare, manufacturing, and telecommunications.
It will be important for engineers and organizations to know the design, purpose, and applications of battery backup systems so that they can sustain performance and prevent outages in power-dependent operations.
Let’s begin with the basics and functions of UPS!
Basics and Function of UPS Systems
An UPS power supply is a system that converts and stores electronic energy which will provide power to a load in the event that the input power source has failed or is not stable and reliable.
Unlike standby generators, which require a time delay to start and to supply power to loads, a battery backup provides instantaneous power transition that uses the internal energy storage devices typically batteries, supercapacitors, or flywheels.
The fundamental uses of a UPS are:
- Power Preservation – Helps ensure essential services continue being functional and operating if an outage occurs.
- Power Management – Providing clean and regulated power to the load while eliminating voltage sags and surges.
- Data Reliability – protection of data loss or corruption from computers, servers, and the communication network.
- Equipment Lifespan – Reducing excessive wear and tear of sensitive devices caused by electrical noise and instability.
Fundamental Design and Components of a UPS
A surge protector is created with several essential components that must work together to efficiently store, convert, and deliver energy. Key components of the UPS power supply in Australia include:
Rectifier/Charger
It converts AC from the utility source into DC for charging the batteries and supplying the inverter.
Battery Bank
The batteries act as an energy storage medium in the system; they typically consist of lead-acid or lithium-ion cells. The batteries provide the alternative power to the connected load during failure of input supply. The capacity of the battery simply determines the backup duration and load handling capability.
Inverter
The inverter receives the storage DC power from the batteries and re-converts it to the AC power required by the connected loads. It ensures the output voltage and frequency constantly remain within limits despite varying load conditions.
Static Switch or Transfer Switch
The function of the static switch (or transfer switch) is to manage the transition from utility to battery power. The static switch ensures instantaneous switchovers without power interruptions.
Control Circuitry and Monitoring System
A modern UPS incorporates microprocessor-based control circuitry to monitor power quality, battery health, and load conditions.The control circuitry may also provide alarms and communication data for the purpose of tracking system performance and scheduled maintenance to maximize its function and reliability.
Types of UPS Systems
The configuration of Uninterruptible Power Supply will be dependent upon the type of power quality desired and the level of protection required. There are three basic types of systems:
- Offline
- Line-Interactive
- Online or Double-Conversion
Operation and Function
Under normal conditions, utility-power is flowing through to the inverter, where it is charging the batteries and supplying power to the inverter for constant stable AC power to the load. In case of a power failure or disturbance, the inverter will draw energy from the batteries to supply a seamless transition of power service. When utility power is returned, the UPS will return to its normal operation and recharge the batteries automatically.
Some battery backup designs can include more sophisticated designs with energy-efficient options and intelligent load management, as well as other energy-efficient features. It can even interface with a BMS or IT assets in the building structure to monitor energy efficiency. Many modern UPS systems are modular or expandable, giving an option of an easy upgrade versus starting from scratch when expansion occurs.
Applications of UPS Systems
Power protection systems are used in many industries that require uninterrupted or highly reliable power supply.
- Information Technology and Data Centers
- Healthcare and Hospitals
- Telecommunications
- Industrial and Manufacturing Facilities
- Financial Institutions
- Home and Office
Final Thoughts
The Uninterruptible Power Supply is more than a backup device.It is a crucial cornerstone of power reliability and electronic protection. By ensuring operational continuity within critical infrastructures, power outage solutions provide energy storage, power conditioning, and intelligent control.
As technology continues to evolve, new designs for uninterruptible power supplies, are becoming more efficient, smaller, and incorporated into smart energy management systems. Today, when non-stop power is something we all need to make productivity possible, engineers and users should understand at least some of the fundamentals with UPS design, the way it functions, and how it can be applied.