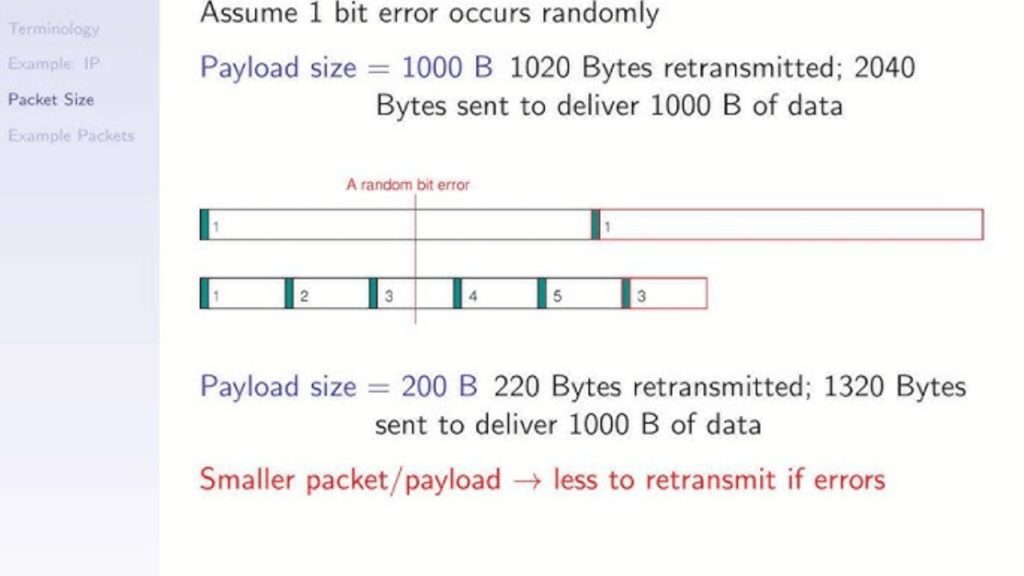
In the world of networking, speed and efficiency are everything. Data zips across the internet in neatly structured packets, but not all packets are created equal. Enter the kilo packet—a term that might not be on every IT professional’s radar but plays a crucial role in optimizing network performance.
Let’s put it into perspective. A single network packet typically ranges from a few bytes to a few kilobytes, depending on the protocol in use. But when we scale up data transmission, managing thousands of these packets efficiently becomes a challenge. That’s where kilo packets come in. Understanding their function is critical for network engineers, cybersecurity experts, and IT administrators who aim to minimize latency, improve throughput, and enhance data handling efficiency.
So, what exactly is a kilo packet, and why should you care? Whether you’re troubleshooting network congestion or optimizing large-scale data transfers, mastering this concept can give you an edge.
Let’s break it down and see how kilo packets impact modern networking.
Understanding Kilo Packets in Networking
A kilo packet, as the name suggests, refers to a data packet that is optimized for efficient bulk transmission, typically aggregating smaller packets for better throughput. This concept is vital in environments where large amounts of data need to be transferred with minimal overhead.
How Do Kilo Packets Work?
- Packet Aggregation: Instead of sending thousands of smaller packets, a kilo packet combines them into a larger unit, reducing transmission overhead.
- Optimized Bandwidth Usage: By grouping multiple data units into a single kilo packet, networks experience fewer interruptions and better efficiency.
- Lower Latency: Fewer packets mean fewer processing instances, reducing delays in data transmission.
- Error Reduction: Kilo packets help minimize packet loss, as fewer, larger packets reduce the risk of fragmented transmissions.
Why Are Kilo Packets Important?
Kilo packets play a crucial role in high-speed networking environments, including cloud computing, video streaming, and enterprise data centers. They ensure data moves smoothly, avoiding bottlenecks that can cripple network performance.
Key Benefits of Kilo Packets:
- Enhanced Throughput: Larger packets translate to fewer transmission events, improving overall speed.
- Reduced Processing Load: Fewer packets mean less work for network hardware, leading to more efficient data handling.
- Improved Network Stability: Aggregating packets helps avoid congestion and improves flow control.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Efficient packet management reduces bandwidth costs and server load.
Use Cases for Kilo Packets
Understanding where and how kilo packets are used can help IT professionals optimize their network strategies.
1. Data Centers and Cloud Networking
Large-scale cloud services and data centers rely on kilo packets to efficiently move terabytes of data across distributed systems. Aggregated packets improve data transfer rates and minimize processing delays.
2. Streaming Services
Platforms like Netflix and YouTube require seamless video delivery. By utilizing kilo packets, these services reduce buffering times and enhance user experience.
3. Enterprise Networks
Corporate networks handling large file transfers benefit from kilo packets by reducing server load and ensuring smooth data exchanges.
4. High-Performance Computing (HPC)
Supercomputers and AI-driven research centers require rapid data movement. Kilo packets help optimize these high-bandwidth processes.
Challenges and Considerations
While kilo packets offer many advantages, they come with challenges:
- Fragmentation Risks: If a large packet is lost, it results in a greater data loss compared to smaller packets.
- Hardware Compatibility: Not all networking hardware optimally supports kilo packet aggregation.
- Security Concerns: Large packets can be targeted for attacks like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS).
- Optimization Complexity: Fine-tuning packet aggregation requires expertise and monitoring.
How to Optimize Networks for Kilo Packets
To make the most of kilo packets, IT teams can follow these best practices:
1. Use Quality of Service (QoS) Policies
Define network priorities for kilo packets to ensure smooth traffic flow and minimal congestion.
2. Implement Adaptive Packet Aggregation
Adjust packet sizes dynamically based on network conditions to maintain performance.
3. Leverage Advanced Routers and Switches
Ensure networking equipment supports large packet transmission to fully utilize kilo packets.
4. Monitor and Analyze Traffic
Use network analytics to identify the best scenarios for kilo packet deployment.
5. Enhance Security Measures
Deploy deep packet inspection (DPI) and firewalls to prevent potential security threats targeting large packet transmissions.
Future of Kilo Packets in Networking
With the rise of AI, 5G, and edge computing, kilo packets will continue to be a vital part of data transmission strategies. Emerging technologies such as Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) are increasingly leveraging kilo packets for efficient traffic management.
As businesses move towards ultra-fast data exchanges, understanding and implementing kilo packet strategies will become an essential skill for IT professionals. Whether in cloud computing, high-performance networking, or streaming services, optimizing packet transmission will remain a key focus area.
Conclusion
Kilo packets are a game-changer for efficient data transfer in modern networks. By reducing transmission overhead, improving throughput, and minimizing latency, they enable seamless connectivity across industries. While challenges exist, proper network optimization strategies can help maximize their benefits. As technology advances, staying ahead of networking trends—including kilo packet optimizations—will be crucial for businesses and IT professionals looking to maintain competitive, high-performance infrastructures.